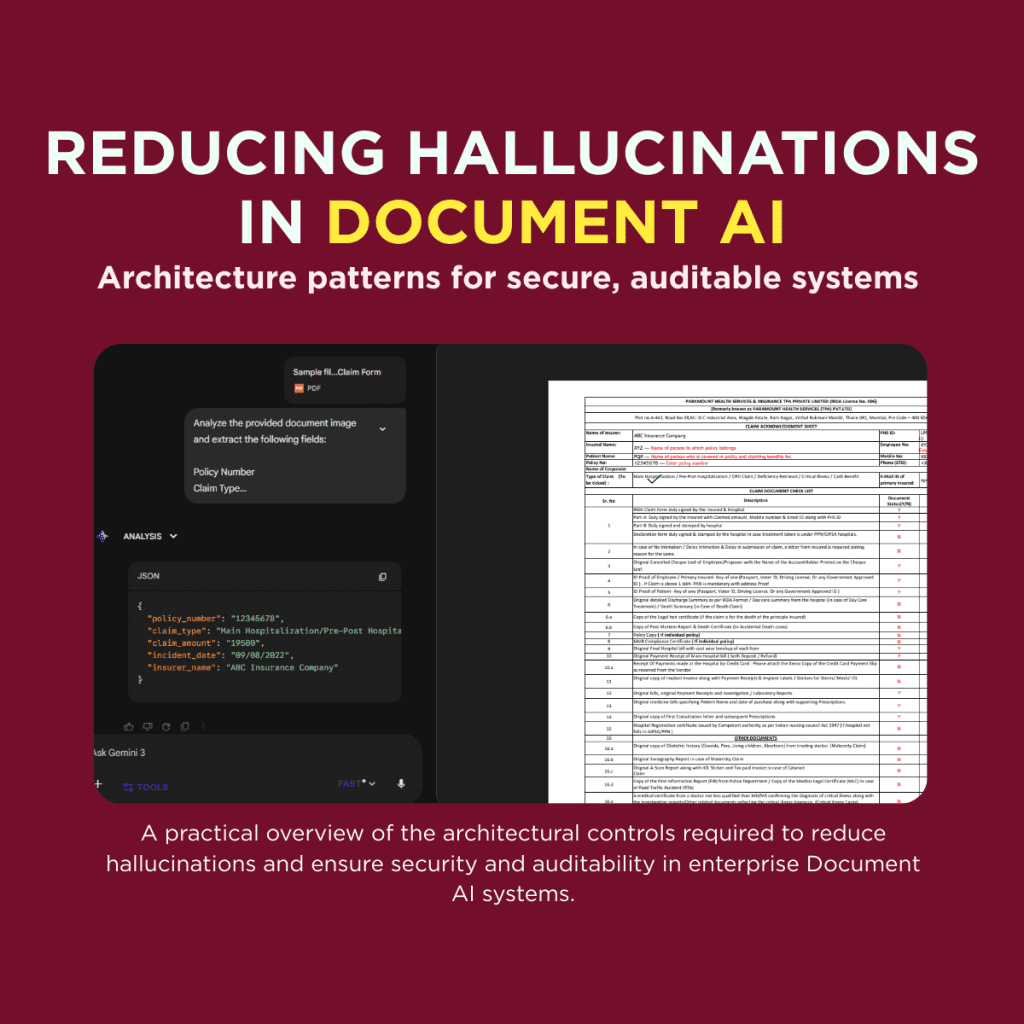
Enterprise Document AI architectures are rapidly evolving beyond traditional OCR toward Vision Language Models (VLMs) and agentic AI systems that can interpret complex layouts, reason over multimodal inputs, and automate end-to-end document workflows. While these approaches unlock significantly higher accuracy and automation, they also introduce new architectural failure modes that are especially critical in enterprise and regulated environments.
In practice, three concerns dominate production deployments: hallucination mitigation, data security, and auditability. If a Document AI system cannot reliably ground outputs in source documents, enforce strong data isolation, and produce a verifiable chain of custody for every extraction, it fails core enterprise requirements—regardless of model quality. This article examines how modern Document AI architectures address these constraints through system-level design choices, not model selection alone.
1. What is hallucination & how to mitigate it in Document AI systems?
In document intelligence, a hallucination occurs when a model produces output that is syntactically correct and plausible, but not grounded in the source document.
Common manifestations include:
-
fabricating values that are not visually present,
-
inferring relationships that do not exist,
-
producing structurally valid but incorrect tables or fields.
Hallucinations are especially common in documents with complex layouts, low-quality scans, mixed modalities, or ambiguous visual cues. As a result, mitigating hallucination risk is a prerequisite for deploying VLMs and agentic systems in real-world enterprise pipelines.
Hallucination mitigation cannot rely on a single technique, because failure modes differ across layouts, document quality, and extraction stages. Production systems typically combine prompt-level controls, architectural safeguards, and verification loops.
1.1 Expert prompt engineering
Prompt design remains one of the most effective and lowest-latency methods to reduce hallucinations in VLM-based extraction.
Effective prompts typically:
-
enforce strict output schemas (e.g., JSON with required fields),
-
restrict outputs to visually verifiable information only,
-
define format, range, and validation constraints explicitly.
In a documented TRM Labs deployment, expert prompt engineering improved usable extraction accuracy from ~80% to 98%, while achieving 100% structural consistency. While prompting alone is insufficient, it establishes a reliable baseline and significantly reduces downstream correction load.
1.2 Self-Correction and Verification loops
Single-pass extraction is fragile under layout variance and scan noise. Production systems therefore introduce multi-step verification and self-correction workflows.
These architectures allow the system to:
-
detect broken or misaligned table structures,
-
identify field–value mismatches,
-
repair corrupted rows or columns,
-
selectively re-run extraction on low-confidence regions.
A representative example is agentic OCR pipelines, such as Reducto’s Agentic OCR, which apply iterative correction loops to validate and refine outputs. Related approaches include self-reflective agents, where the system critiques its own reasoning and regenerates outputs when inconsistencies are detected.
While these mechanisms increase latency, they dramatically improve reliability and are essential for regulated environments.
1.3 Model-level architectural techniques
Some hallucination mitigation strategies operate directly at the inference architecture level, rather than through orchestration alone.
A notable example is Visual Contrastive Decoding (VCD). VCD compares model outputs generated from:
-
the original document image, and
-
a visually distorted version of the same image.
Predictions that are inconsistent across these visual conditions are suppressed, reducing object-level hallucinations and anchoring outputs more firmly in actual visual evidence. Techniques like VCD shift hallucination mitigation from heuristics toward model-aligned constraints.
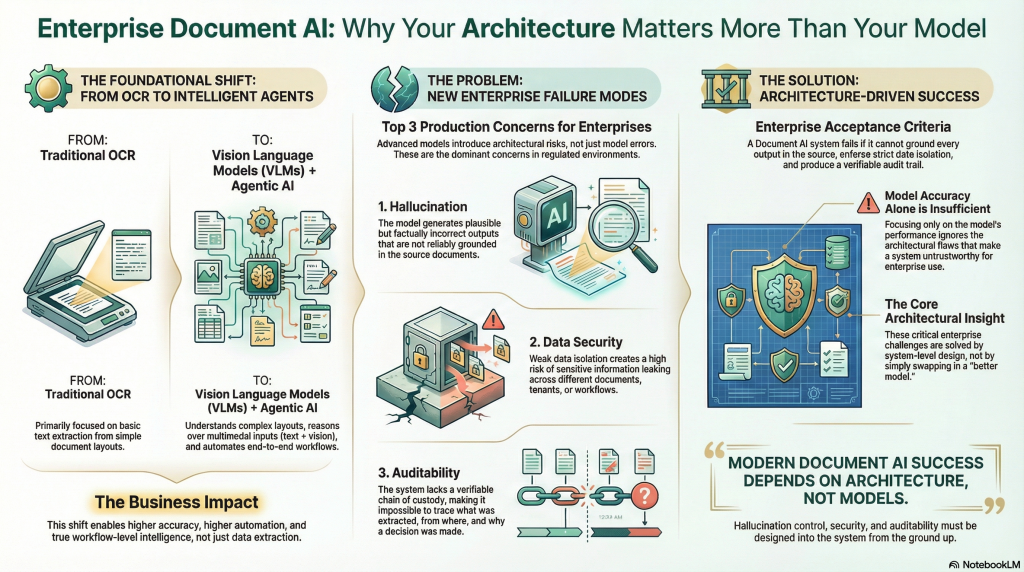
2. Security and traceability in Document AI systems
Deploying VLMs and agentic systems in pipelines that process sensitive documents—including financial records, medical files, and regulatory submissions—requires a security-by-design approach. Security controls must be foundational, not optional.
2.1 Zero data retention (ZDR)
Zero Data Retention (ZDR) is a baseline requirement when using third-party AI models.
ZDR ensures that:
-
input documents are not stored,
-
prompts and outputs are not logged,
-
data is never used for model training.
ZDR is enforced through a combination of contractual guarantees and technical controls. Without it, sensitive enterprise data may persist beyond organizational boundaries.
2.2 Secure sandbox execution environments
VLM and agentic workflows should execute inside isolated sandbox environments with strict network egress controls.
These sandboxes:
-
block all unauthorized outbound connections,
-
prevent data exfiltration even under prompt injection attacks,
-
neutralize entire classes of model-manipulation exploits.
Even if a model is coerced into unsafe behavior, the surrounding infrastructure ensures that sensitive data cannot leave the system perimeter.
2.3 Immutable chain of custody and auditability
For regulated industries, every extraction must be fully auditable and reproducible.
A robust document AI pipeline maintains an immutable internal chain of custody that records:
-
the source document or image,
-
the exact model and version used,
-
the prompt, plan, or agent configuration executed,
-
the final verified output.
This guarantees a forensically sound record of how each data point was produced—critical for audits, legal disputes, and regulatory review.
In our earlier post, Best Document AI Approach in 2026: OCR, VLMs, or Agentic Systems?, we compared the strengths and trade-offs of different document extraction approaches.
This article focuses on what comes after that decision.
Once VLMs or agentic systems are introduced into production pipelines, hallucination risk, security controls, and auditability become the dominant challenges. These are not model-level issues—they are architectural ones. Without explicit grounding, verification, and security-by-design, even highly accurate systems fail to meet enterprise and regulatory requirements. The practical takeaway is simple: choosing the right document AI approach is necessary, but engineering it correctly is what determines whether it can be trusted in production.
If you’re evaluating document AI for a real production workflow and want to sanity-check architectural decisions, you can explore our case studies or reach out to discuss a specific use case.